Kafka-partitions/replicas分配策略
为了更好的做负载均衡,Kafka尽量将所有的Partition均匀分配到整个集群上。Kafka分配Replica的算法如下:
-
将所有存活的N个Brokers和待分配的Partition排序
-
将第i个Partition分配到第(i mod n)个Broker上,这个Partition的第一个Replica存在于这个分配的Broker上,并且会作为partition的优先副本
-
将第i个Partition的第j个Replica分配到第((i + j) mod n)个Broker上
假设现在有5个Broker,分区数为5,副本为3的主题,按照上面的说法,主题最终分配在整个集群的样子如下:
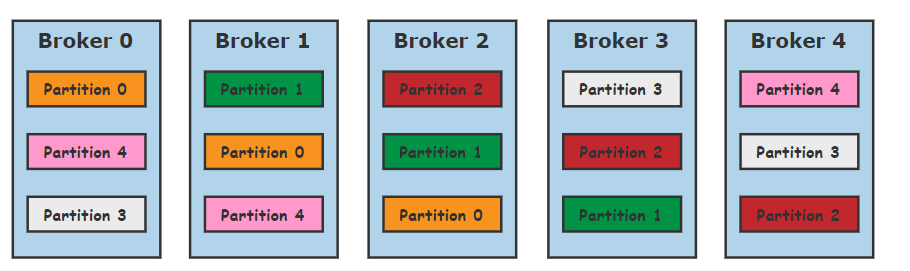
按照这种算法,会存在以下明显几个问题:
-
所有主题的第一个分区都是存放在第一个Broker上,这样会造成第一个Broker上的分区总数多于其他的Broker,这样就失去了负载均衡的目的
-
如果主题的分区数多于Broker的个数,多于的分区都是倾向于将分区发放置在前几个Broker上,同样导致负载不均衡
Kafka 内部将分区分配到各个 Broker 中的具体算法实现函数就是assignReplicasToBrokers
def assignReplicasToBrokers(brokerList: Seq[Int],
nPartitions: Int,
replicationFactor: Int,
fixedStartIndex: Int = -1,
startPartitionId: Int = -1)
: Map[Int, Seq[Int]] = {
if (nPartitions <= 0)
throw new AdminOperationException("number of partitions must be larger than 0")
if (replicationFactor <= 0)
throw new AdminOperationException("replication factor must be larger than 0")
if (replicationFactor > brokerList.size)
throw new AdminOperationException("replication factor: " + replicationFactor +
" larger than available brokers: " + brokerList.size)
val ret = new mutable.HashMap[Int, List[Int]]()
val startIndex = if (fixedStartIndex >= 0) fixedStartIndex else rand.nextInt(brokerList.size)
var currentPartitionId = if (startPartitionId >= 0) startPartitionId else 0
var nextReplicaShift = if (fixedStartIndex >= 0) fixedStartIndex else rand.nextInt(brokerList.size)
for (i <- 0 until nPartitions) {
if (currentPartitionId > 0 && (currentPartitionId % brokerList.size == 0))
nextReplicaShift += 1
val firstReplicaIndex = (currentPartitionId + startIndex) % brokerList.size
var replicaList = List(brokerList(firstReplicaIndex))
for (j <- 0 until replicationFactor - 1)
replicaList ::= brokerList(replicaIndex(firstReplicaIndex, nextReplicaShift, j, brokerList.size))
ret.put(currentPartitionId, replicaList.reverse)
currentPartitionId = currentPartitionId + 1
}
ret.toMap
}
private def replicaIndex(firstReplicaIndex: Int, secondReplicaShift: Int, replicaIndex: Int, nBrokers: Int): Int = {
val shift = 1 + (secondReplicaShift + replicaIndex) % (nBrokers - 1)
(firstReplicaIndex + shift) % nBrokers
}
从上面的算法可以看出:
-
副本因子不能大于 Broker 的个数;
-
第一个分区(编号为0)的第一个副本放置位置是随机从 brokerList 选择的;
-
其他分区的第一个副本放置位置相对于第0个分区依次往后移。也就是如果我们有5个 Broker,5个分区,假设第一个分区放在第四个 Broker 上, 那么第二个分区将会放在第五个 Broker 上;第三个分区将会放在第一个 Broker 上;第四个分区将会放在第二个 Broker 上,依次类推;
-
剩余的副本相对于第一个副本放置位置其实是由 nextReplicaShift 决定的,而这个数也是随机产生的
如果考虑机架的话,假设 startIndex = 4,fixedStartIndex = 1。现在如果我们有两个机架的 Kafka 集群,brokers 0,1 和 2 同属于一个机架; brokers 3, 4 和 5 属于另外一个机架。现在我们对这些 Broker 进行排序:0, 3, 1, 4, 2, 5(每个机架依次选择一个Broker进行排序)。 按照机架的 Kafka 分区放置算法,如果分区0的第一个副本放置到broker 4上面,那么其第二个副本将会放到broker 2上面,第三个副本将会放到 broker 5上面; 同理,分区1的第一个副本放置到broker 2上面,其第二个副本将会放到broker 5上面,第三个副本将会放到 broker 0上面。 这就保证了这两个副本放置到不同的机架上面,即使其中一个机架出现了问题,我们的 Kafka 集群还是可以正常运行的。现在把机架因素考虑进去的话,我们的分区看起来像下面一样:

只要上面其中一个机架没有问题,我们的数据仍然可以对外提供服务。这就大大提高了集群的可用性。






